NDIR Measurement Principle
NDIR stands for Non Dispersive Infra Red. With this measurement technique, the concentration of a gas can be determined in a simple and relatively inexpensive way. By using multiple measuring cells, multiple gases can also be analyzed.
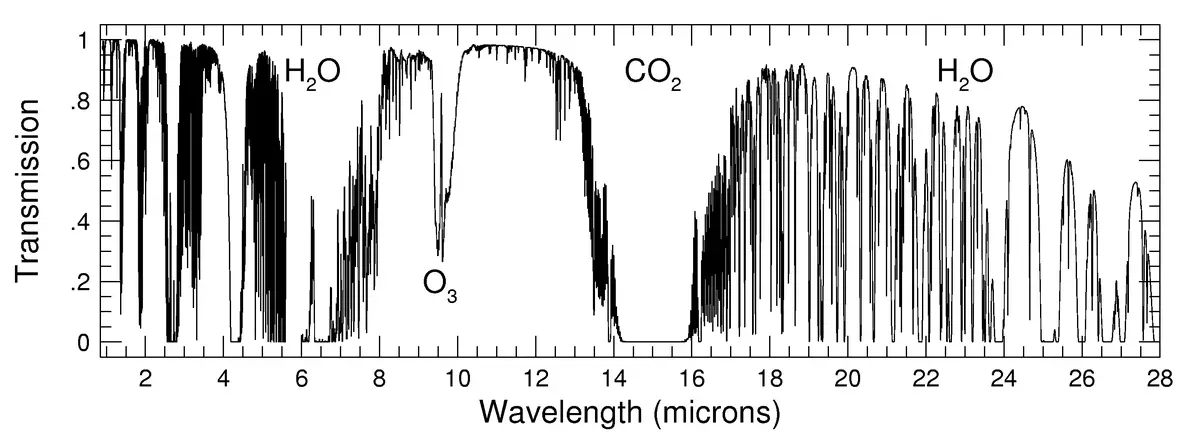
Molecules with a sufficiently large dipole moment absorb infrared light. The absorbed energy is converted into motion between the various atoms in the molecule. The degree of absorption depends on the atoms in the molecule and the type of bond between the atoms. Examples of molecules that strongly absorb IR light include water (H2O), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). The graph shows the infrared spectrum of part of the atmosphere:
Gas Concentrations
The absorption spectrum depends on the different existing bonds/functional groups between the atoms and their interaction with infrared light. A molecule with different bonds absorbs infrared at different wavelengths, resulting in multiple absorption peaks in the spectrum. To determine the concentration of a molecule, a specific part of the spectrum is selected. This absorption spectrum then contains a characteristic peak of the molecule. The wavelength is chosen so that other substances present do not interfere and the absorption peak belongs solely to the substance being analyzed. To obtain infrared light with the correct wavelength, a lens with a filter is used that only transmits the desired wavelength. The measurement range of the NDIR depends on the length of the measuring cell — the longer the cell, the higher the chance that a molecule will be detected.
The degree of light absorption is directly proportional to the concentration according to the Beer-Lambert Law.
A schematic layout of a gas analysis infrared cell is as follows:

Accuracy
The sample passes through a measuring cell in which the infrared light is absorbed. Mirrors are often used to effectively extend the measuring cell. The light beam then passes back and forth through the cell several times before reaching the detector. Before detection, an optical filter is used to select the correct wavelength. Only the specific wavelength is detected at the detector. To increase accuracy, multiple optical filters can be used and placed sequentially in front of the detector and/or a permanent reference measurement can be used. Maintaining a constant temperature of the measuring cell and applying pressure corrections also contribute to improved accuracy.
Multi-Gas Analyzer
NDIR is a proven technique and often very suitable for single-component online gas concentration measurements. NDIR cells are used for many applications in safety detection, workplace monitoring, process monitoring, and environmental measurement. In many applications, the measurement principle is implemented with multiple cells and combined with other techniques within one instrument or setup: a multi-gas analyzer.
