Advanced Gas Filter Correlation Infrared Optics for Gas Analysis
Introduction to Gas Filter Correlation Infrared Optics
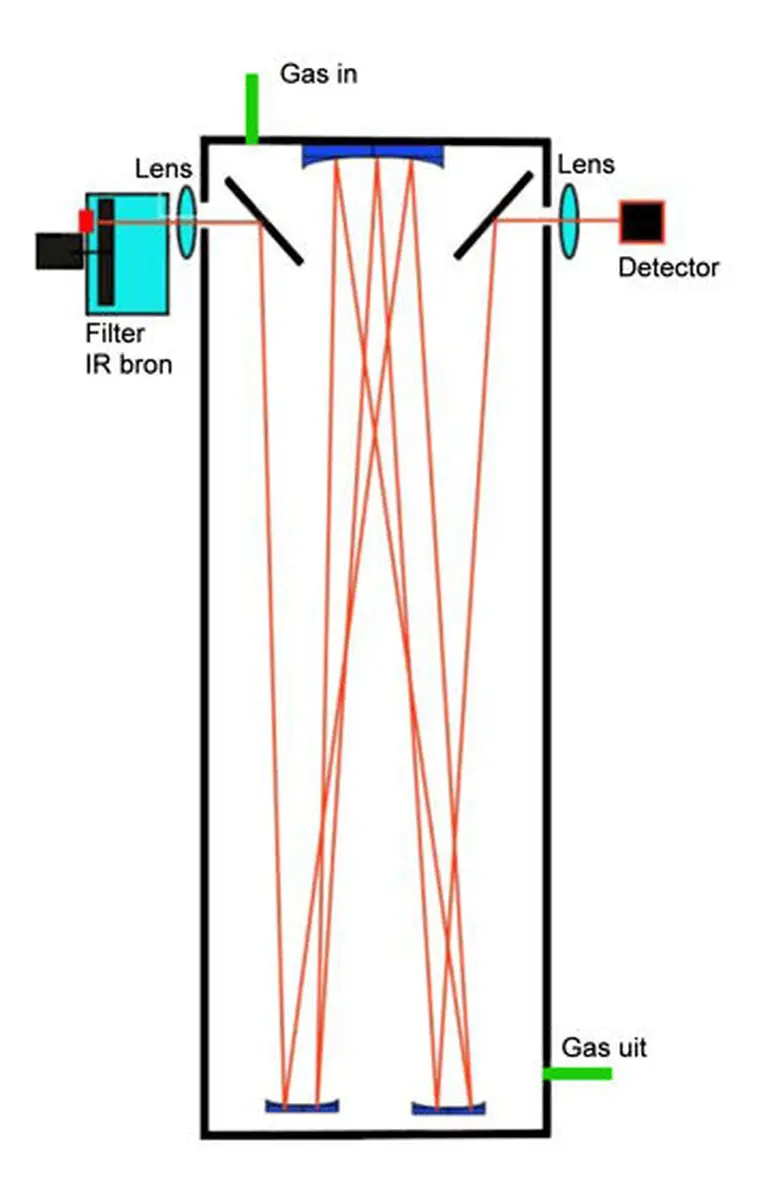 Gas Filter Correlation infrared optics is a highly selective measurement technique for specific gases. By selecting the appropriate wavelength, it becomes possible to eliminate interfering gases. The detection limits of gases are determined by the distance the infrared light travels within the measurement cell. Traditional infrared analyzers are equipped with a measurement cell that has an optical path length of approximately 25 cm. This limited length typically allows for a full-scale range of around 100 ppm for CO2 with a minimum detection limit of 0.5 ppm.
Gas Filter Correlation infrared optics is a highly selective measurement technique for specific gases. By selecting the appropriate wavelength, it becomes possible to eliminate interfering gases. The detection limits of gases are determined by the distance the infrared light travels within the measurement cell. Traditional infrared analyzers are equipped with a measurement cell that has an optical path length of approximately 25 cm. This limited length typically allows for a full-scale range of around 100 ppm for CO2 with a minimum detection limit of 0.5 ppm.
Quantum Measurement Cell for Lower Detection Limits
To achieve lower detection limits, the Quantum measurement cell was developed. This cell combines the benefits of a GFC measurement cell with an optical path length of 400 cm. In practice, this enables a minimum detection limit of 50 ppb for CO2. Similar improvements can be achieved for other infrared-absorbing gases.
Advantages of the Quantum Bench
Some key advantages of the Quantum bench:
• Small dead volume of 300 ml;
• Fast response time <60 seconds;
• Suitable for many infrared-absorbing gases;
• Highly suitable for CO2, CO, CH4, SF6, SO2, and NOx;
• Very stable signal with minimal drift;
• Highly selective;
• Optical path length of 400 cm;
• Very compact design;
• Linear output;
• Low maintenance requirements.
